Medication non-adherence leads to poor treatment outcomes, avoidable hospitalizations, an estimated 125,000 deaths annually, and U.S. healthcare costs of up to $300 billion. Medication adherence is a heavily weighted factor in the CMS Medicare Advantage and Part D Star Ratings. While pharmacies are not directly rated by CMS star ratings for medication adherence, they can influence and help improve star ratings.
This article explores how pharmacies can affect star ratings and how medication adherence tools, such as smart pillboxes using remote therapeutic monitoring, can help improve star ratings for Medicare plans.
CMS Star Ratings and Medication Adherence
Star ratings are used by CMS to evaluate the performance of Medicare Advantage plans. For Medicare Advantage Plan Part D, CMS rates the plans, but not pharmacies directly. However, pharmacy performance can improve star ratings and medication adherence through the following measures.
- Diabetes medications
- Hypertension (RAS antagonists)
- Cholesterol (statins)
Together, these three measures make up over 30% of the overall Medicare Part D star rating. Improved medication adherence directly contributes to higher star ratings, which can lead to increased financial incentives for healthcare providers. Pharmacies that help patients stay adherent can therefore help improve star ratings.
Because pharmacists see patients frequently, they are in the unique position to extend their role far beyond the counter and influence medication adherence, which leads to better patient outcomes.
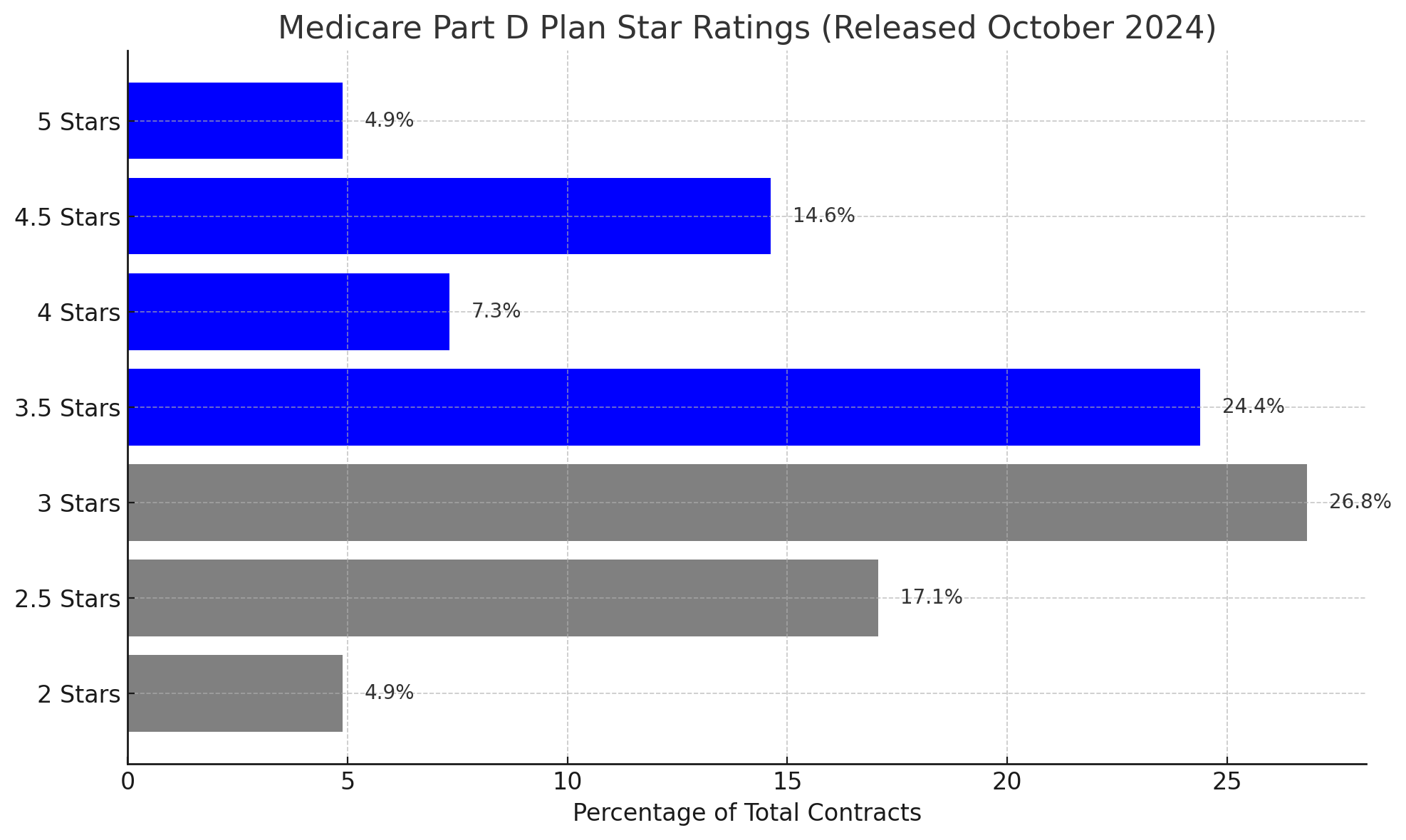
The 2025 Medicare Advantage and Part D plan star ratings, released in October 2024, have improved post-COVID-19, but are still lower than pre-pandemic. Only 4.9% of plans achieved the full 5-star rating, while the majority clustered between 3.0 and 3.5 stars.
How Pharmacies Can Improve Star Ratings
A 2024 study published in the American Journal of Managed Care analyzed over 100,000 Medicare Advantage enrollees and found a relationship between missed CMS star ratings, adherence measures, and increased healthcare utilization and costs. Patients taking medications for diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia were tracked over three years for medication adherence. Adherence was defined as at least 80% of days covered annually for each medication class.
The research showed that the more adherence measures missed, the higher the risk of emergency department (ER) visits, inpatient stays, and avoidable hospitalizations. Missing just one of the nine possible adherence measures reported a 12% to 26% increased risk of hospital and ER use. When patients missed four or more measures, risk jumped to as high as 50%. These patients also faced 11% to 20% higher monthly healthcare costs compared to the fully adherent patients.
This study reinforces that missing adherence impacts CMS star ratings for medication adherence directly and drives up clinical costs. For plans to achieve or maintain 4- or 5-star status, sustained performance on adherence measures is a must. And for pharmacies and providers, this study highlights the ROI of patient support programs that help close adherence gaps over time.
Independent Pharmacies vs. Major Chains
Both independent and major chain pharmacies contribute to pharmacy star ratings. Independent pharmacies often outperform chains in personalized adherence interventions because they develop strong patient relationships within their communities. In rural areas, they help overcome access barriers that might otherwise impact adherence. Frequent patient interactions and close community ties make independent pharmacies well-positioned to influence health outcomes and improve star ratings.
Source: Pharmacy Quality Alliance (PQA)
RTM and Medication Adherence to Improve Star Ratings
Medication adherence tools help track how consistently patients follow their prescribed regimens. These tools collect data, analyze trends, and support targeted medical interventions. Remote therapeutic monitoring (RTM) allows clinicians and contracted pharmacists to monitor medication-taking behavior using connected smart devices.
Common examples of remote therapeutic medication monitoring devices are:
- Smart pillboxes
- Smart Inhalers
- Smart BottleCaps
- Mobile apps
Improving medication adherence can be the difference between a Medicare Part D plan earning a 3-star or 4-star rating. A study published in the Journal of Managed Care & Specialty Pharmacy found that pharmacist-led adherence programs significantly increased patients’ ability to take their medications enough to meet the 80% standard set by CMS.
Plans earning 4 stars or higher qualify for quality bonus payments from CMS. A 5% bonus on the base per-member payment can yield millions in additional annual revenue. Pharmacies that consistently support medication adherence directly help Part D plans qualify for and maintain these rewards..
Understanding How Pharmacies Can Affect Star Ratings
Pharmacies are uniquely positioned to influence CMS star ratings for medication adherence. Though not rated by CMS themselves, their frequent patient interactions and growing use of remote therapeutic monitoring medication adherence tools allow them to improve star ratings and patient outcomes. In a chronic heart failure study, high adherence even to a placebo had a greater impact on survival than some low-active treatments. This is an example of the profound effect of consistent medication-taking behavior. By helping patients stay on track, pharmacies can help close adherence gaps, raise star ratings, and contribute to better health and lower costs across Medicare populations.